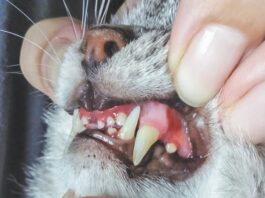
When They Went to the ER for Cat Bites
A three-year retrospective study of people who went to the Mayo Clinic Hospital in Rochester, Minn., with cat bites to their hands found that 30 percent of them required hospitalization. While dog bites can seem dramatic, with torn skin, broken bones and considerable bleeding, their open wounds can often be easier to clean — and heal.
Evaluating a Human Drug for Feline Heart Disease
Veterinarians are increasingly using a human drug to prevent arterial thromboembolism — a blood clot interrupting blood flow — in cats. The clots are common in feline heart disease, and their presence carries a guarded to poor prognosis: more than 60 percent of cats don’t survive them. In addition, because cats who do survive often develop a second clot, usually causing extreme pain and paralysis of the rear limbs, many are euthanized.
Short Takes: April 2014
A lack of knowledge about cats’ reproduction and the myth that cats should have a first litter before spaying may lead to 200,000 accidental litters — and more than 850,000 kittens — annually in the U.K.
Short Takes: March 2014
The American Pet Product Manufacturers Association issues its National Pet Owners Survey every two years — a real door-stopper with more than 500 pages. The findings are intended for businesses, marketers and media. Here’s a sampling from the 2013-14 section about cat owners, who comprise 37 percent of U.S. households.
Dispelling the Many Myths About Their Body Language
Do you know what message your cat sends when his tail stands upright? A survey of 1,100 owners in England found that 75 percent of them didn’t realize that an upright tail meant the moggy — their slang for cat — was sending a greeting.
Unwelcome Petting Can
Cause Stress, a Study SaysThis will come as a shock to owners who enjoy petting their cats. Some cats like being petted and purr in delight; others only tolerate it. In fact, according to a study by an international team of animal behaviorists, when owners impose themselves on cats to pet them, the cats experience stress and release hormones linked to anxiety.
The Message Worth Repeating: Leave No Pet Behind in a Disaster
At one point when rushing rivers flooded Colorado towns and farms earlier this year, 2,000 stranded people and 500 pets were evacuated by helicopter. The swift, rising water caused loss of life and damage to 2,380 acres in the state. The American Humane Association and other organizations on the ground rescued hundreds of pets and livestock.
58 MPH Sounds Fast, but Grip and Maneuverability Play Key Roles
Cheetahs, our domestic cats’ big cousins, seem to fascinate scientists. Maybe it’s because they’re the fastest land animal, and measuring their speed presents a challenge. Researchers have clocked cheetahs running after a lure and observed films of them chasing prey in the wild.
Short Takes: September 2013
The sad truth about cats’ access to veterinary care in the U.S.: They don’t have much. Surveys show that nearly twice as many dogs visit the veterinarian as cats, even though the cats outnumber dogs — 86 million versus 78 million. Thirty-nine percent of owners say they would take their cat to the veterinarian only in the event of illness; and 60 percent report that their cat hates going to the veterinary clinic. The visits may stress both owners and cats, says the American Association of Feline Practitioners. To offer a more calming, encouraging environment, it has launched an initiative to improve cats’ treatment, handling and overall health.
A Single Gene Keeps Mice Away From Cats
A specific gene affecting a mouse’s sense of smell helps it avoid predatory cats, according to research at Northwestern University. Neurobiologist Thomas Bozza, Ph.D., and his team found that removing an olfactory receptor responsible for detecting certain odors can impact a mouse’s survival. The gene, TAAR4, controls production of a receptor that detects a substance concentrated in carnivores’ urine. Usually, mice avoid the scent marks of predators, but those lacking the TAAR4 gene do not — and can end up as prey.
Singles Turn to Pets for a Sense of Family
An intriguing trend has developed among singles in the U.S. Single people — men particularly — are becoming pet owners at rates greater than families. They’re “turning to pets for love and a sense of family,” according to a survey by the American Veterinary Medical Association. In a five-year period, pet ownership among the never married, widowed and divorced grew 16.6 percent. Excluding people who never married, growth in pet ownership among singles rose 17.7 percent during this same period.
Short Takes: June 2013
Obesity among pets in the U.S. continued to climb in 2012, with the number of overweight cats reaching an all-time high. Veterinarians reported that 58.3 percent of their feline patients — up from 55 percent over the previous year — were overweight or obese in the sixth annual survey by the Association for Pet Obesity Prevention (APOP). Given the cat population of 74.1 million in this country, that equals about 43.2 million cats, the association says. Surprisingly, the survey also revealed a “fat gap,” according to APOP founder Ernie Ward, DVM. When veterinarians asked owners to describe their fat cats’ body condition as too thin, normal, overweight or obese, 45.3 percent said normal.