A cat’s kidneys can be enlarged due to inflammation, infection, cysts, urinary tract obstruction, or masses (potentially cancerous). Toxins and infections also may cause acutely enlarged kidneys. Treatment starts with determining the underlying cause and analyzing signs of disease.
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs of renal (kidney) disease commonly start gradually and can be easily missed. Cats with kidney problems often drink more than usual and either urinate more or, in advanced cases, less than normal. A decreased appetite and lethargy/depression are not specific to renal disease, but they do indicate that your cat is not feeling well. You may also notice:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Drooling
- Bad breath
- Painful abdomen
- Weight loss
Cats with acute disease generally get taken to the veterinary hospital right away, while slowly developing enlarged kidney cases may go months before any problem is noted.
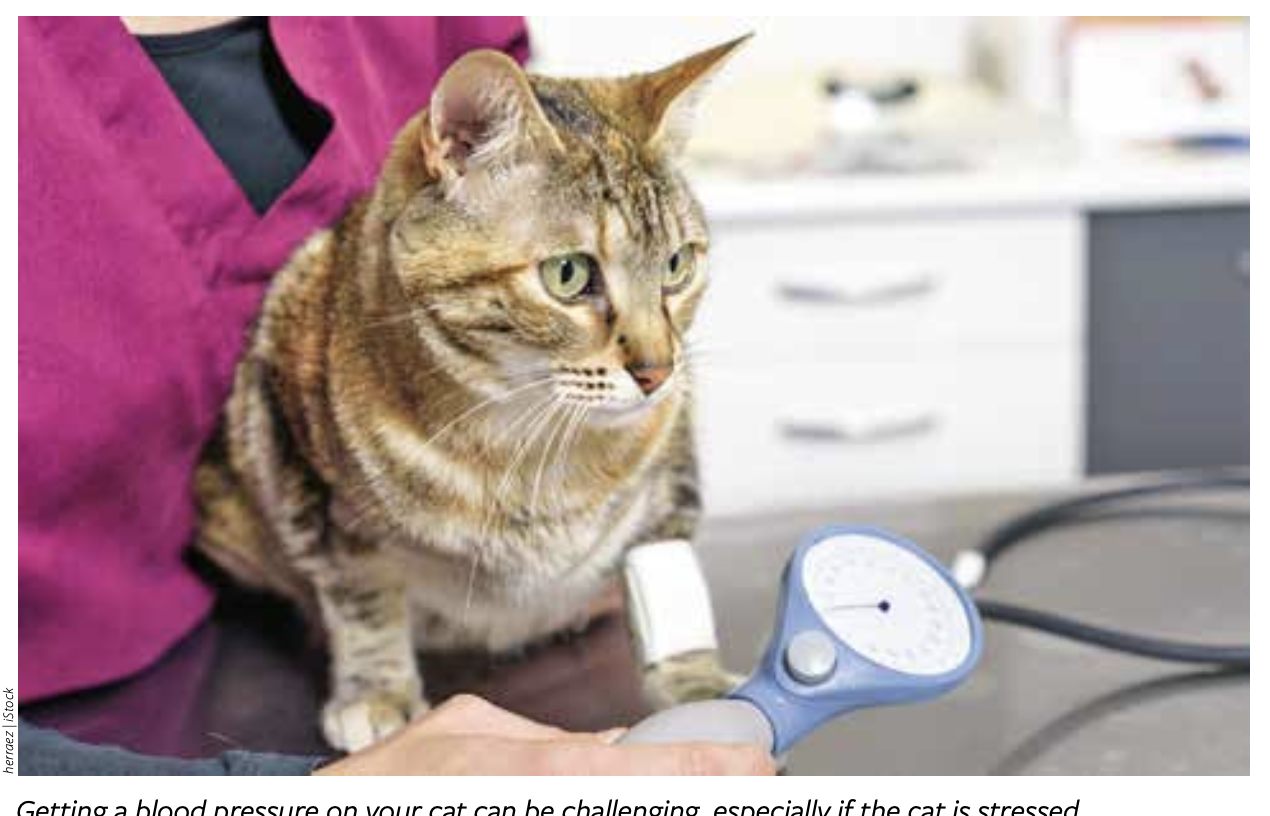
Blood Pressure Is a Big Concern
Hypertension is a serious condition that is often missed since its clinical signs are often not obvious, says Bruce Kornreich, DVM, PhD, director of the Cornell Feline Health Center at Cornell University’s College of Veterinary Medicine and editor-in-chief of Cornell CatWatch. The relationship between kidney problems and hypertension in cats is close, says Dr. Kornreich, as “74% of hypertensive cats are azotemic (have renal problems), and between 19% and 65% of cats with chronic kidney disease are hypertense,” says Dr. Kornreich.
Signs of hypertension in your cat may include increased drinking and urinating due to the kidney damage, sudden blindness (retinal detachment), hemorrhage within the eye/dilated pupils, ataxia/seizures/disorientation/depression (neurologic signs), and possibly increased respiratory rate and effort (heart failure secondary to myocardial hypertrophy), says Dr. Kornreich. It is amazing how many body systems can be affected by feline kidney disease and the hypertension it often causes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis starts with a physical examination. Your veterinarian may palpate an enlarged kidney as an incidental finding (no clinical signs), or it might be noted in a cat with symptoms of illness. Some cats will have just one enlarged kidney while both will be big in others. Rarely, one will be enlarged while the other is small and often scarred.
Your thorough history, including what signs you have noticed and for how long, is important. Next, a serum biochemistry and complete blood panel are often submitted to look for any evidence of electrolyte/mineral disturbances, accumulation of waste products that are normally removed from the blood by the kidneys, and other organ dysfunction. Most senior cats will (and should) have a blood pressure check done as part of their examination.
A urinalysis is crucial, and a bacterial culture may be recommended to rule out bacterial or fungal infection of the urinary tract. Radiographs and/or an ultrasound can help to further characterize the structure of the kidneys (i.e., to distinguish a diffusely enlarged kidney from a kidney with multiple cysts, as is seen with polycystic kidney disease). A biopsy (generally a needle biopsy but a surgical biopsy may be recommended) can be taken to provide a diagnosis.
Once all the diagnostic information is collected, your veterinarian can hopefully determine the cause and design a therapeutic plan.
Treatment
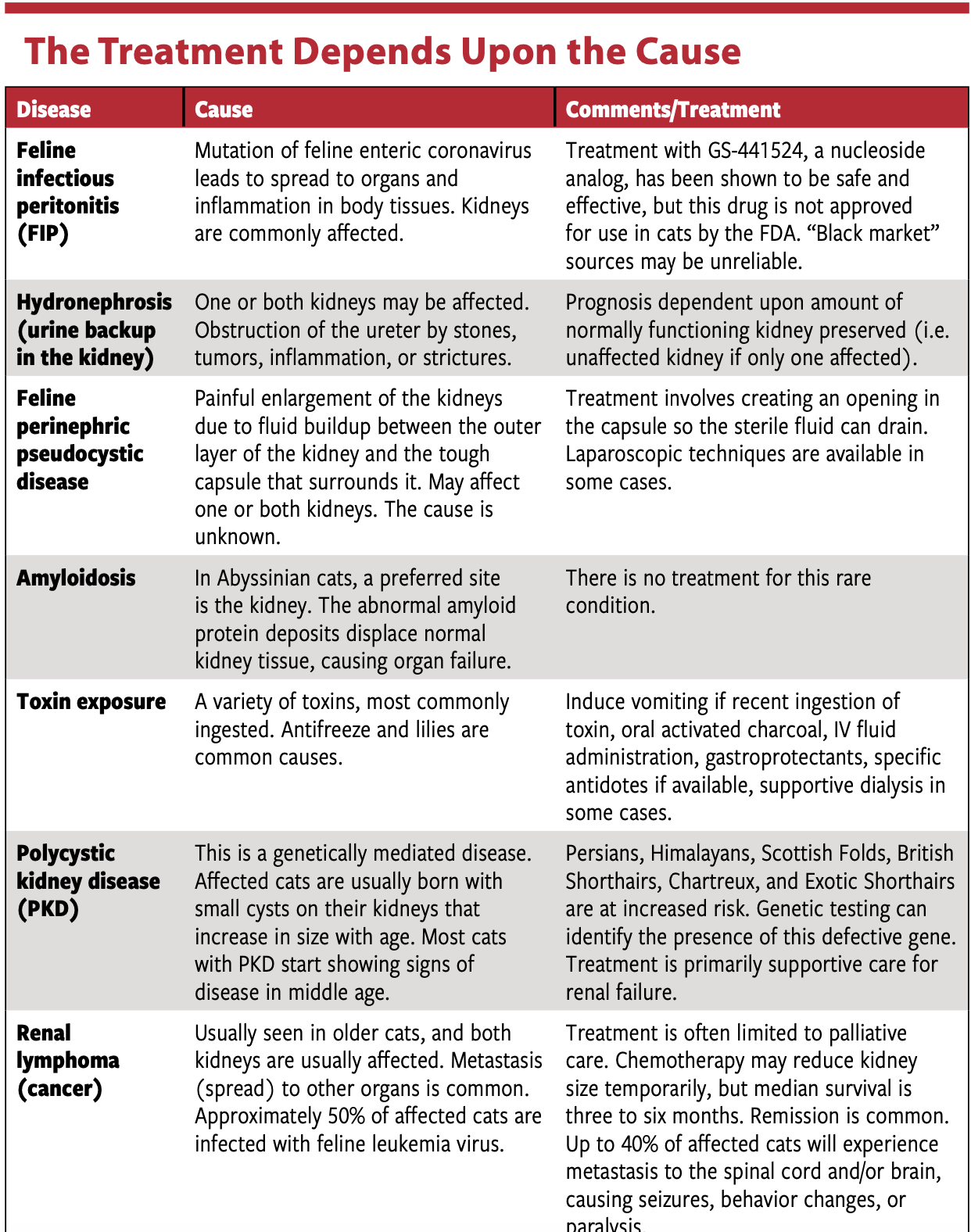
Treatment depends upon the cause (see chart). If one kidney is damaged from trauma or a kidney stone, that one may shrink as it scars down. The remaining kidney will often enlarge somewhat as it takes on full “renal duties” for your cat. Cats can do just fine with one healthy kidney.
Kidney Failure
The treatment of cats with kidney failure is primarily supportive, and any related health problems, such as hyperthyroidism and hypertension, must be treated and hopefully controlled.
Fluid therapy helps maintain hydration and helps your cat’s damaged kidneys flush out metabolic wastes and toxins. Prompting adequate water intake is crucial, and many owners can give their cats subcutaneous fluids at home to address this issue. Depending on disease severity, dietary recommendations (i.e., protein, phosphorus, and sodium restriction, antioxidant supplementation) may be made to ease the burden on the kidneys.
Hemodialysis, a process in which waste products/toxins are removed from the blood by a machine before being returned to the body, is an option for some cases of acute kidney injury that need support while damaged kidneys heal, but it is generally not recommended for feline patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This technology requires specific expertise and equipment, and is currently only available at select referral and academic institutions.
If only one kidney is diseased and it presents a threat to the other kidney or other organs (i.e., cancer metastasis), surgical removal may be suggested. Early intervention for a blockage of a ureter that may predispose to hydronephrosis (stretching/swelling of the kidney due to the build-up of urine that cannot drain from it due to obstruction) could be curative but requires a skilled surgeon and supportive veterinary team.
Transplants
Some institutions offer kidney transplants for cats with CKD, but this surgery is not without its challenges, is quite costly, and patients require lifetime follow-up medications and management following a successful kidney transplant. In most cases, donor cats (i.e., those donating a healthy kidney) must be identified by the owner of the cat requiring a transplant, and in many cases, shelter cats are used as donors. The donor cats are thoroughly health tested, and the family of the recipient cat is usually required to adopt the donor cat or find it an appropriate home. Since cats can do quite well with just one kidney, this can be a costly but effective option for a cat with end stage renal disease and no other options.